Request for a call today
Wheel Hub Bearings: The Invisible Guardian of Automotive Driving Safety
 2025.08.15
2025.08.15
 Industry News
Industry News
Among the countless components in a car, the wheel hub bearing is perhaps the least well-known, yet it carries a crucial mission. It connects the wheel to the body, supporting the vehicle's entire weight while also withstanding impacts from the road and lateral forces from the vehicle's body, ensuring stable wheel operation at high speeds. The performance of the wheel hub bearing is directly related to the vehicle's handling, safety, and comfort, making it an indispensable "joint" in the vehicle's driving system.
The Core Function and Structural Secrets of the Wheel Hub Bearing
The core function of the wheel hub bearing is to perfectly integrate the rotation of the wheel with support from the vehicle body. It must simultaneously withstand radial and axial loads—radial loads from the vehicle's own weight and the reaction forces from the road during driving, and axial loads from cornering, acceleration, and braking. This dual load requirement necessitates extremely high precision and durability in the wheel hub bearing's structural design.
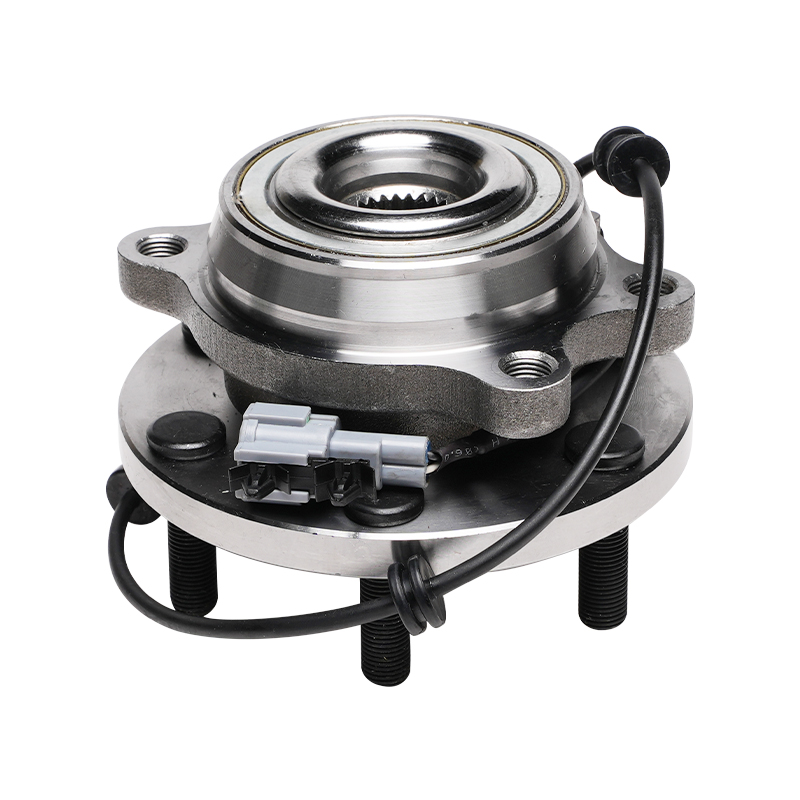
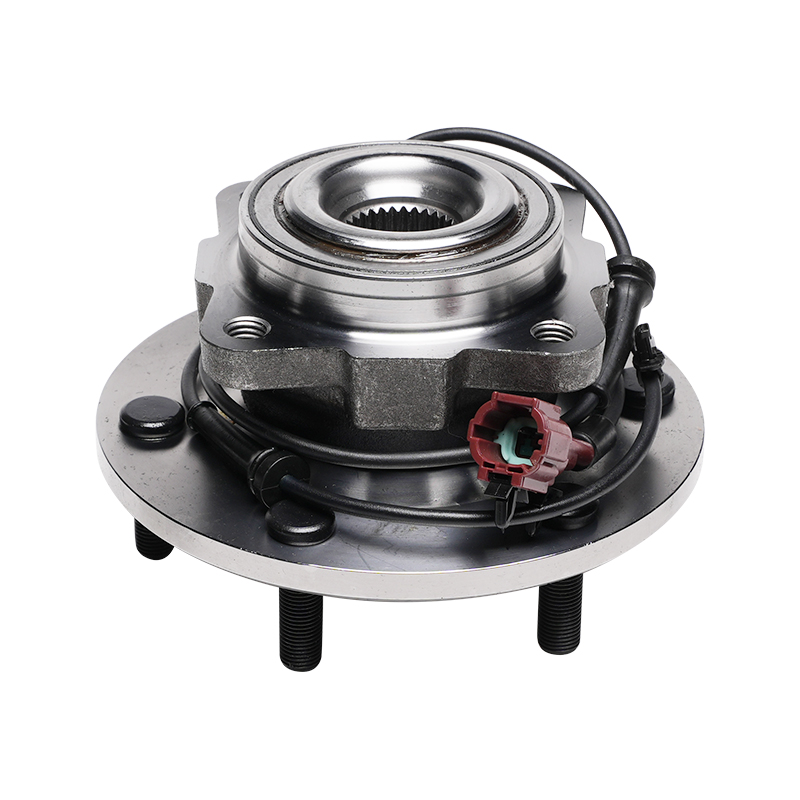
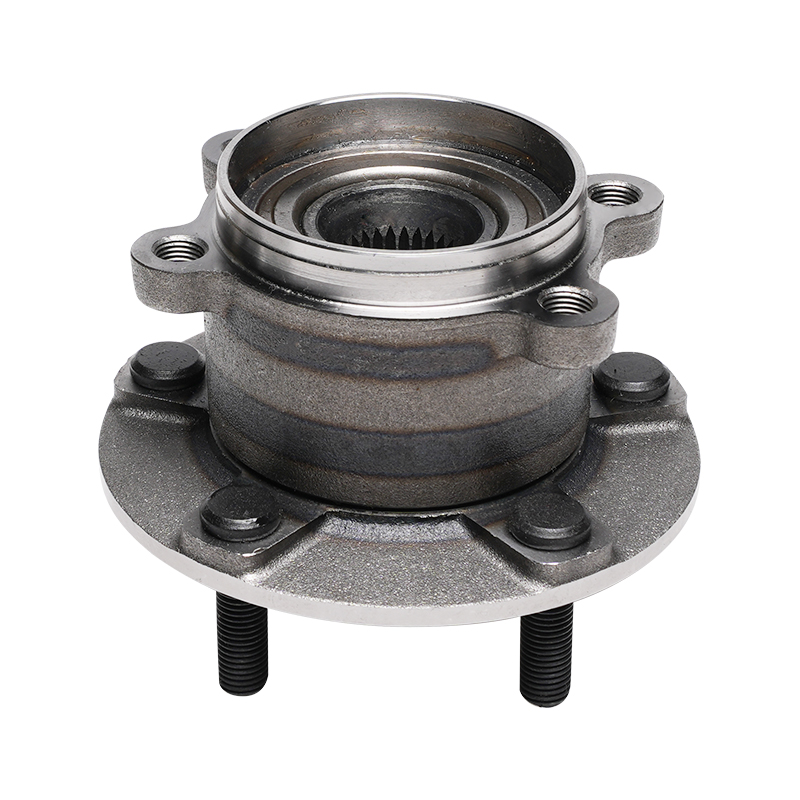
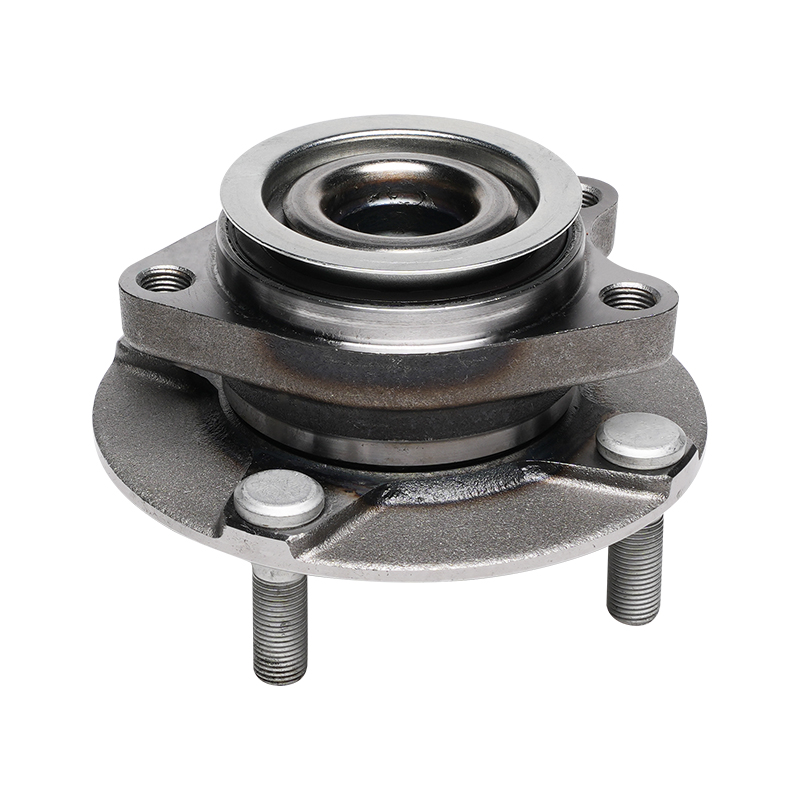
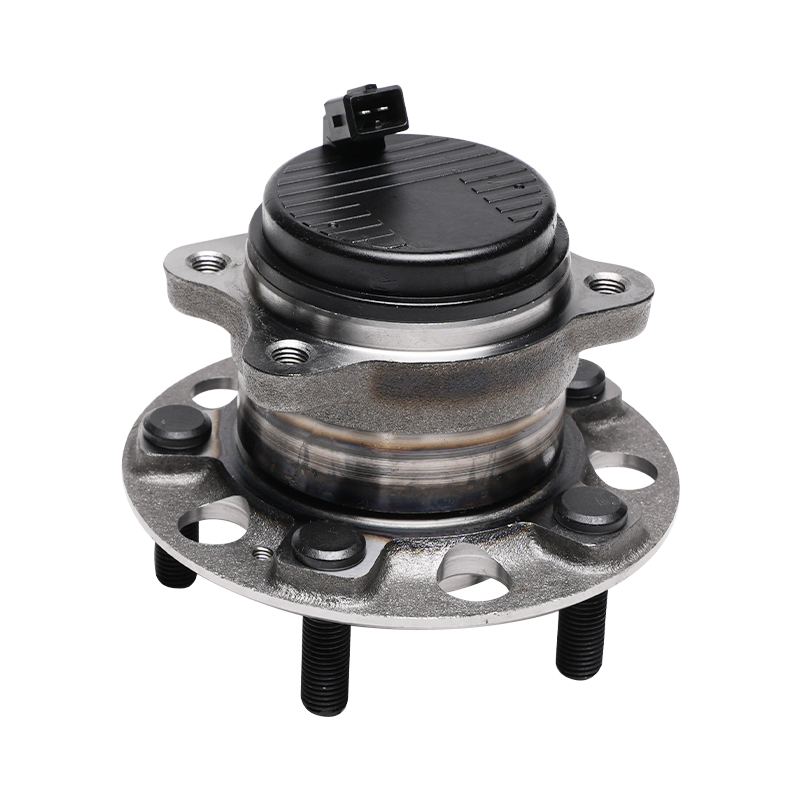
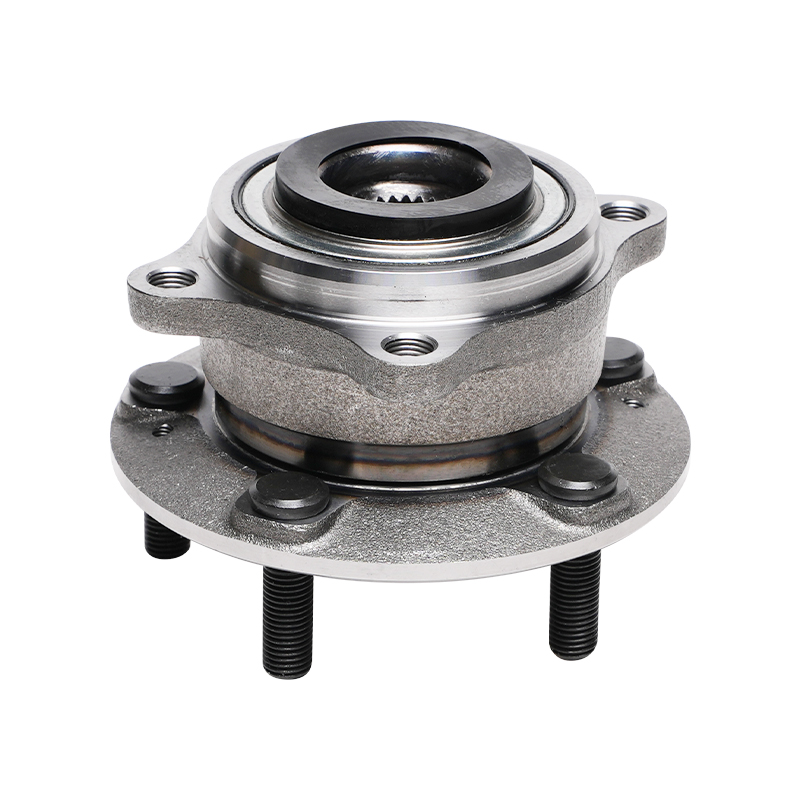
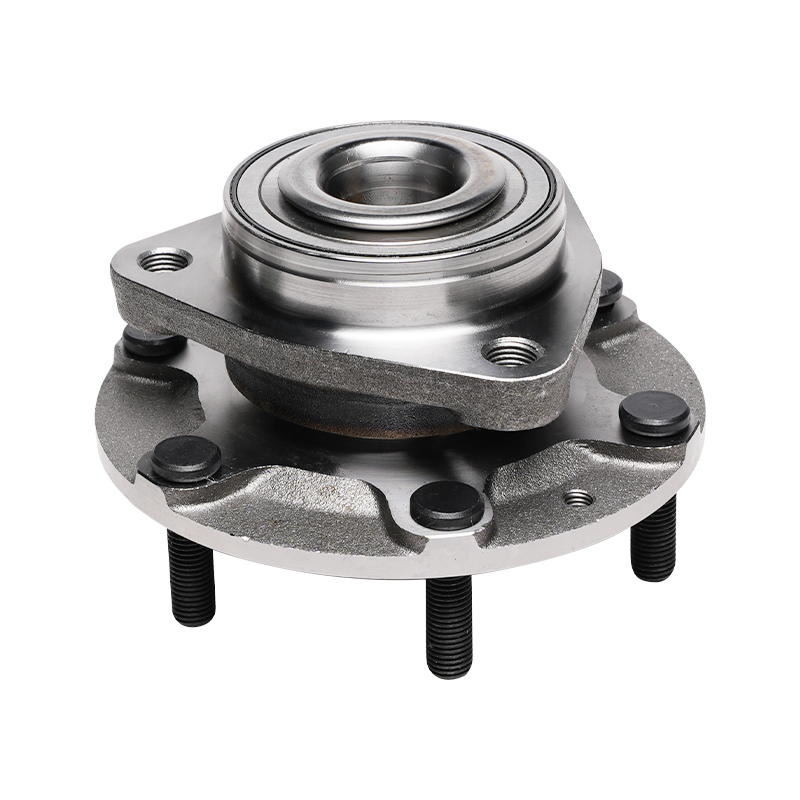
Structurally, modern automotive wheel hub bearings often utilize a modular design, integrating components such as the bearing, flange, and sensor into a compact unit. This integrated design not only simplifies the installation process but also reduces component mismatch and improves overall rigidity. It typically consists of an inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and a cage. The shape of the rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) is optimized based on the load requirements of different vehicle models to ensure even stress distribution and reduce wear under various operating conditions.

Sealing technology is another key feature of wheel hub bearings. Exposure to complex driving environments, wheel hub bearings must withstand corrosion from dust, mud, water, and salt, while also preventing internal grease leakage. Advanced sealing structures utilize multi-layer lip seals and a special grease formulation to achieve effective sealing while reducing friction loss, ensuring long-term bearing operation.
Technological Iteration: A Leap in Performance from Separate to Integrated
The development of the automotive industry is driving continuous innovation in wheel hub bearing technology. Early wheel hub bearings were mostly split-body structures, requiring separate assembly with the wheel hub and axle end. This not only complicated the installation process but also easily compromised stability due to loose components during driving. With increasing demands for automotive safety and reliability, integrated wheel hub bearing units have emerged.
This new wheel hub bearing unit integrates the bearing with the wheel hub, flange, and other components into a single unit. Through precise interference fits and bolted fastening, it ensures stability under high-speed rotation and complex loads. Furthermore, this unitized design reduces the number of parts and minimizes assembly errors, thereby extending the overall service life.
Advances in material technology have also laid the foundation for improved wheel hub bearing performance. Currently, the inner and outer rings of wheel hub bearings are mostly made of high-strength alloy steel. Through specialized heat treatment processes, they achieve high strength while maintaining excellent toughness and wear resistance. Rolling elements are often made of high-purity bearing steel, precision-machined to ensure roundness and surface finish, thereby reducing friction and vibration during operation.
Performance Test: Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Environments
The diverse driving environments of automobiles place severe demands on the performance of wheel hub bearings. In high-temperature environments, wheel hub bearings can heat up due to frictional heat generation, which not only affects the performance of the grease but can also reduce the strength of the material. Therefore, wheel hub bearings must possess excellent high-temperature resistance. By optimizing heat dissipation structures and selecting grease with high-temperature stability, they ensure proper operation even during extended high-speed driving or hill climbing.
Low-temperature environments also pose a significant challenge for wheel hub bearings. Low temperatures increase the viscosity of the grease, leading to increased starting resistance and reduced material toughness, increasing the risk of brittle fracture. To cope with low-temperature operating conditions, wheel hub bearing grease must exhibit excellent low-temperature fluidity to ensure rapid formation of an effective lubricating film even at low temperatures. Furthermore, the bearing material must undergo special treatment to enhance its impact resistance in low-temperature environments.
In addition to temperature fluctuations, road bumps and impacts are also common challenges for wheel hub bearings. When driving on uneven roads, wheels are subjected to impact forces from all directions, which can cause the wheel hub bearings to experience instantaneous peak loads. To withstand these impacts, the wheel hub bearing's structural design must provide sufficient rigidity and impact resistance. By optimizing the contact area and shape between the rolling element and raceway, impact loads can be distributed and localized stress concentrations can be reduced. Maintenance and Care: Key to Extending Service Life
While modern wheel hub bearing units offer high reliability and durability, proper maintenance and care remain crucial to extending their lifespan. Avoid prolonged driving in harsh road conditions to reduce the impact and wear on the wheel hub bearings. Regular inspection of the wheel hub bearings is also crucial.

During routine inspections, if you notice unusual noises (such as humming or squealing) while driving, or if your vehicle experiences stuttering or swerving when steering, these may indicate wear or looseness in the wheel hub bearings. Visit a professional repair facility for inspection and replacement. When replacing tires or performing chassis repairs, take care to protect the wheel hub bearings and avoid unnecessary impact or collision during installation, which can affect their accuracy and performance.
The lubrication condition of the wheel hub bearings directly impacts their service life. Although sealed wheel hub bearing units are factory-filled with a special grease and require no additional grease during normal use, damage to the seal, allowing grease to leak or contaminants to enter, can seriously affect bearing performance. Therefore, during daily use, wheel hub bearings should be protected from severe impact or scratches to protect the integrity of the sealing structure.
As a core component of a vehicle's driving system, the performance of wheel hub bearings is directly related to the vehicle's safety, comfort, and reliability. With the continuous development of the automotive industry, wheel hub bearings have continued to advance in structural design, material technology, and intelligent technology, providing a solid guarantee for safe driving.