Request for a call today
Wheel Hub Unit: The Core Guarantee of Vehicle Driving Safety and Performance
 2025.09.01
2025.09.01
 Industry News
Industry News
In the automotive chassis system, the wheel hub unit is a key component connecting the vehicle body and wheels, and its performance directly impacts vehicle handling, comfort, and safety. As an integrated component integrating bearings, flanges, and sensors, the wheel hub unit bears the crucial responsibilities of bearing vehicle weight, transmitting driving torque, and maintaining stable wheel rotation. As the automotive industry evolves towards intelligent and lightweight design, the technological content of the wheel hub unit continues to increase, becoming a key indicator of a vehicle's core competitiveness.
Technical Structure and Core Functions of the Wheel Hub Unit
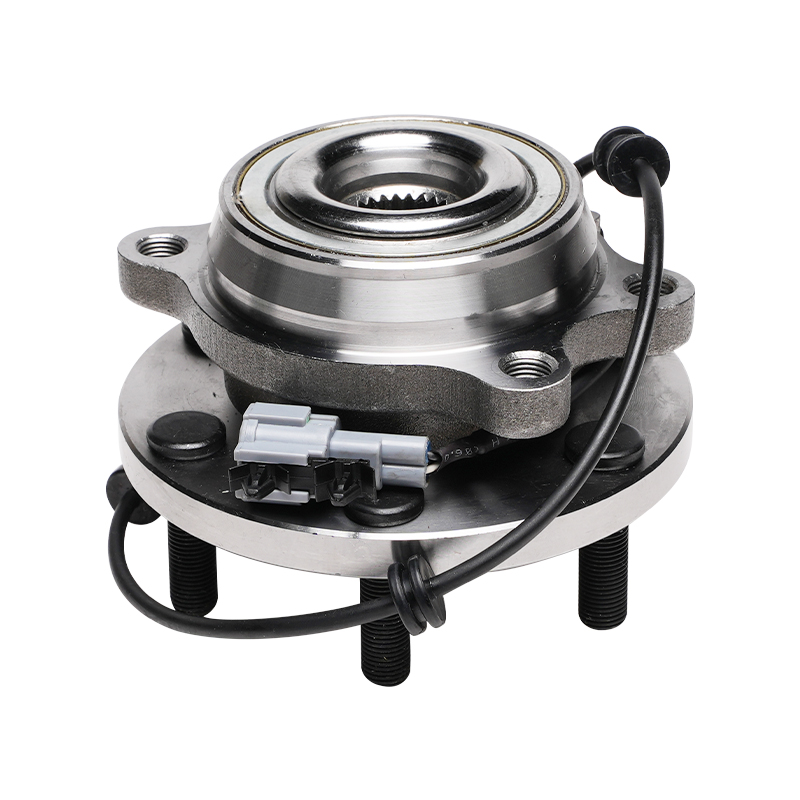
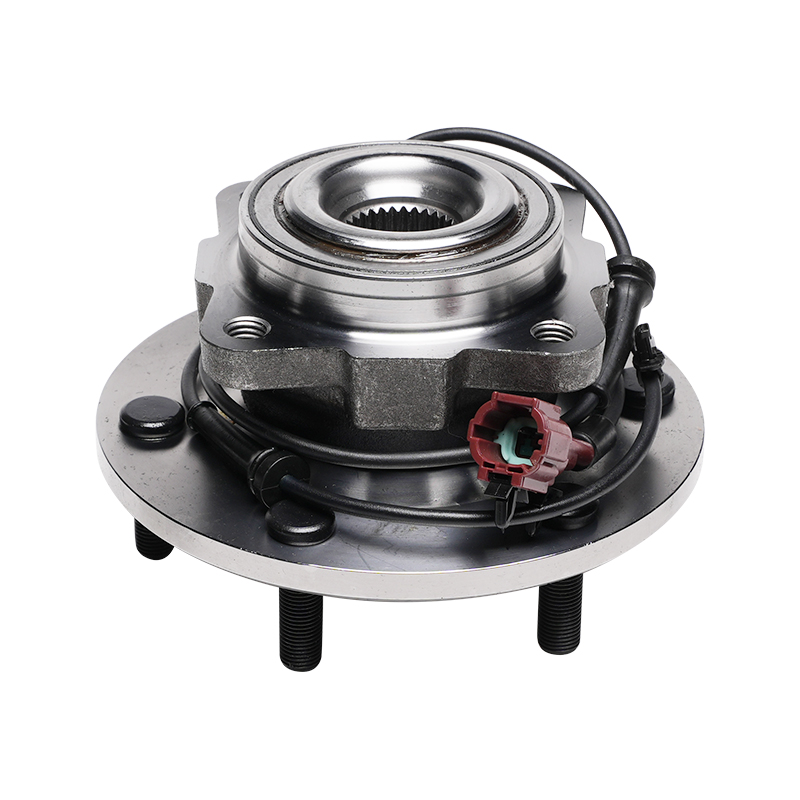
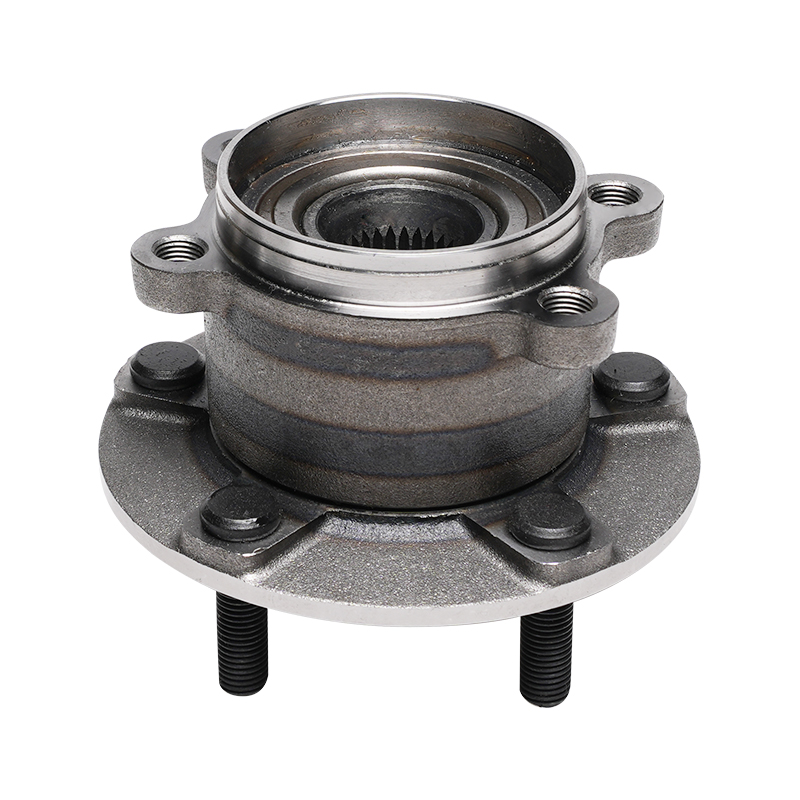
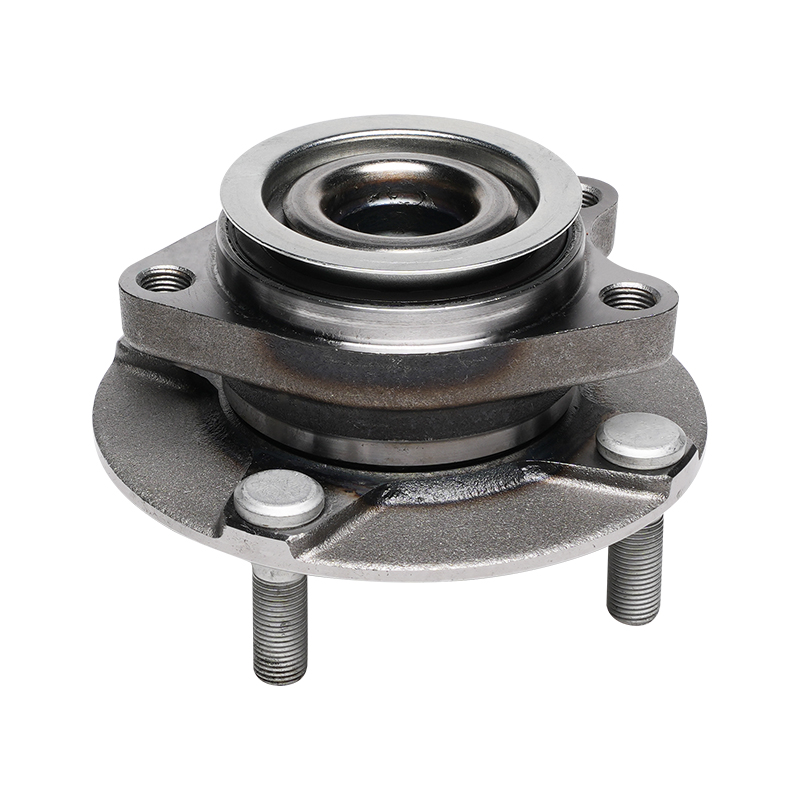
The wheel hub unit is not a single part, but rather a system assembly comprised of multiple precision components working in concert. Its core structure comprises the basic bearing components, including the inner ring, outer ring, rolling elements, and cage. It also incorporates the mounting flange, sealing devices, and sensor modules for monitoring driving conditions. This integrated design not only simplifies vehicle assembly but also significantly improves overall structural stability.
Sealing performance is a key technical indicator of the wheel hub unit. The excellent sealing structure effectively blocks the intrusion of impurities such as dust, mud, and water, while also preventing internal grease leakage, ensuring long-term stable operation of the bearings under complex operating conditions. Modern wheel hub units generally adopt a double-lip seal design with sealing lips made of special materials. This design maintains excellent sealing performance within a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C, adapting to diverse climate conditions and driving environments.

In terms of power transmission, wheel hub units utilize precise tolerances to smoothly transmit engine torque to the wheels while also absorbing impact loads from road bumps. The shape of the rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) is optimized based on vehicle type. Passenger cars often use ball structures to reduce noise, while commercial vehicles tend to prefer roller designs for increased load capacity.
Wheel hub unit performance improvements and technological breakthroughs
With the increasing popularity of new energy vehicles, wheel hub units face greater technical challenges. The higher instantaneous torque output of electric vehicles places even more stringent demands on the strength and responsiveness of wheel hub units. To this end, the industry widely uses high-strength carburized steel as the core material. Through precision heat treatment, the bearing surface hardness reaches HRC58-62, while maintaining excellent core toughness to withstand frequent starts and stops and sudden acceleration and deceleration.
Lightweighting is a key approach to improving vehicle range and handling performance. The lightweight design of wheel hub units focuses on both materials and structure. In terms of materials, replacing traditional steel with high-strength aluminum alloy can reduce component weight by over 30%. In terms of structure, finite element analysis is used to optimize the shape of the flange and bearing seat, eliminating redundant material to further reduce weight while ensuring strength.
Key Points for Wheel Hub Unit Fitting and Maintenance
The performance requirements of wheel hub units vary significantly depending on the vehicle type. Therefore, when selecting a suitable wheel hub unit, comprehensive consideration should be given to factors such as vehicle weight, powertrain type, and operating environment. Passenger cars prioritize comfort and low noise, typically choosing small, high-precision wheel hubs. Commercial vehicles, due to their high load capacity, prioritize high strength and durability. Off-road vehicles require greater impact resistance and sealing performance to withstand complex road conditions.
Proper installation and maintenance are key to ensuring the lifespan of wheel hubs. During installation, tight tolerances must be maintained to avoid premature wear caused by interference or excessive clearance. The bearing seat must also be kept clean to prevent impurities from entering and affecting rotational accuracy. During daily use, the wheel hub seals should be regularly inspected to prevent the ingress of mud and water. Any abnormal noise or vibration should be promptly repaired to prevent further problems.

The lifespan of a wheel hub is closely related to driving habits. Frequent rapid acceleration and deceleration can exacerbate bearing wear, while prolonged driving on bumpy roads can increase impact loads. Proper speed control, avoiding overloading, and choosing high-quality tires can effectively extend the lifespan of the wheel hub and reduce maintenance costs.
As a core component of the automotive chassis system, the technological development of wheel hubs has always been closely linked to the advancement of the automotive industry. From traditional mechanical bearings to modular units with integrated intelligent functions, the evolution of wheel hub units has witnessed the automotive industry's transition from the mechanical age to the intelligent age. In the future, with continuous technological breakthroughs, wheel hub units will play an even more important role in improving driving safety, promoting automotive intelligence, and achieving green travel.