Request for a call today
Core automotive components: Comprehensive analysis of Wheel Hub Bearing
 2025.06.15
2025.06.15
 Industry News
Industry News
In the modern automotive industry, although the Wheel Hub Bearing is often hidden deep inside the wheel, it plays a vital role in vehicle safety and handling. As automotive design develops towards higher speeds and higher performance, higher and higher requirements are placed on the performance, life and stability of wheel hub bearings.
1. What is a wheel hub bearing? Its importance in automobiles cannot be ignored
The wheel hub bearing is a mechanical device connecting the wheel and the axle. It not only supports the rotation of the wheel, but also bears the weight of the vehicle body, absorbs road impact, ensures flexible rotation and transmission accuracy. The working state of the wheel hub bearing directly affects the handling stability, ride comfort and fuel efficiency of the vehicle.
Especially in front-wheel drive models, the front wheel hub bearing integrates multiple loads of the drive shaft, steering system and braking system, and its precision and durability requirements are extremely high. Poor quality or severely worn wheel hub bearings can cause tire shaking, abnormal steering noise and even brake failure, which seriously threatens driving safety.
2. The development history of wheel hub bearings: from the first generation to the third generation
Wheel hub bearings can be divided into the following typical generations according to the degree of structural and functional integration:
1. First generation wheel hub bearings (first generation bearings)
The initial wheel hub bearings are mainly composed of two separate tapered roller bearings, which are installed in the wheel hub by adjusting the axial clearance. They rely on manual installation accuracy and grease sealing effect, and are prone to problems such as large clearance, high noise and short life.
2. Second generation wheel hub bearings (second generation integrated type)
Integrating the inner and outer rings and flanges into one, eliminating the installation and adjustment process, enhancing rigidity and sealing, and greatly improving installation efficiency and service life.
3. Third generation wheel hub bearings (third generation intelligent modularization)
On the basis of the second generation, electronic components such as ABS sensors, magnetic rings, encoders, etc. are further integrated to support high-end functions such as vehicle electronic stability control system (ESC) and automatic driving assistance system.
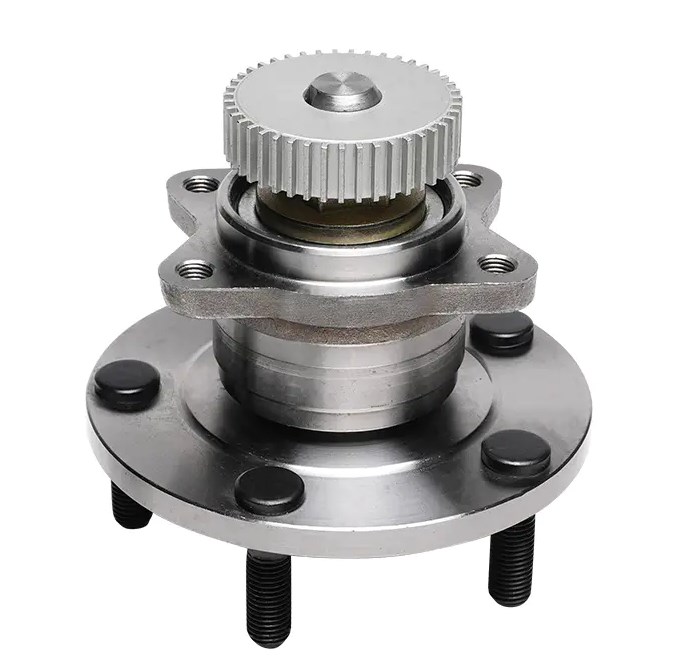

3. Detailed explanation of the working principle and structural composition of wheel hub bearings
The basic structure of wheel hub bearings includes outer ring, inner ring, rolling element (ball or roller), cage, seal and grease. The rolling element rolls freely between the inner and outer rings, achieving high-speed operation of the wheel hub with minimal friction.
The working principle is as follows:
When the car tire rotates with the axle, the wheel hub bearing supports the weight of the entire vehicle body through the rolling element;
The rolling element maintains high-precision operation under high load, different speeds and temperature differences;
The seal ensures that the grease does not leak out and prevents dust and water vapor from entering;
High-performance materials (such as GCr15 bearing steel and ceramic mixed materials) can significantly improve life and wear resistance.
4. Common fault analysis and maintenance suggestions
Once the wheel hub bearing is damaged, it will not only bring safety hazards, but also may cause damage to the vehicle's driving system. The following are several typical fault manifestations:
Abnormal noise: "buzzing" or "chuckle" sounds during steering or driving, which are common in bearing raceway wear or grease failure;
Shaking: The steering wheel vibrates significantly when driving at high speed or braking, which may be abnormal hub clearance or loose bearings;

Heating: Under long-term high-speed operation or overload driving, the bearing temperature rises too fast, which is a signal of grease aging or seal damage.
Maintenance suggestions:
Check the operation of the wheel hub bearing every 30,000 to 50,000 kilometers;
Check the looseness and lubrication status of the bearing when replacing tires or brake systems;
Avoid long-term operation of the vehicle under wading, heavy load, and high temperature conditions;
Choose pre-installed grease sealed bearing components from the original manufacturer or high-quality brands when replacing.
Although the wheel hub bearing is a small component, it is an indispensable "joint" to support the operation of the entire wheel. Understanding its structural principles, mastering usage skills, and choosing high-quality products will directly affect the stability and safety of driving. With the development of vehicle intelligence, wheel hub bearings are also evolving from "mechanical" to "electronic + mechanical" composite, and their technical prospects are unlimited.