Request for a call today
Wheel hub assemblies: the key hub of car driving
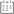 2025.06.08
2025.06.08
 Industry News
Industry News
In the complex structure of the car, although the wheel hub assemblies seem to be just an inconspicuous component, in fact, it plays a vital role in the normal operation, safe driving and overall performance of the car.
1. Definition and composition of wheel hub assemblies
Wheel hub assemblies are important components that connect the tires to the axles of the vehicle. It is like the "skeleton" of the tire, supporting the tire and ensuring that the tire can rotate stably. Generally speaking, the wheel hub assembly is mainly composed of the wheel hub, bearings, seals and other parts. The wheel hub, as the core part, is usually made of metal materials, and its shape and structural design must meet the dual requirements of strength and lightness; the bearing is responsible for reducing the friction when the wheel hub rotates, so that the wheel can rotate smoothly; the role of the seal should not be underestimated, it can effectively prevent dust, moisture and other impurities from entering, protect the bearings, and extend the service life of the wheel hub assembly.
II. Working principle of wheel hub assemblies
When the vehicle is running, the power generated by the engine is transmitted to the wheel hub assembly through the transmission system. With the support of the bearing, the wheel hub can rotate at high speed around the axle, thereby driving the tire to rotate. In this process, the wheel hub not only has to bear the weight of the vehicle itself, but also has to deal with various forces from the road surface, such as braking force during braking and lateral force during turning. The existence of the bearing enables the wheel hub to operate in a relatively low-friction environment, ensuring the flexibility and efficiency of wheel rotation. The seals always stay at their posts to block the invasion of external impurities and maintain a good working environment inside the bearing.

III. Types of wheel hub assemblies
(I) Classification by drive mode
Drive wheel hub assembly: commonly found on the drive wheels of front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive and four-wheel drive vehicles. It not only realizes the rotation of the wheels, but also transmits power from the transmission system to the wheels to drive the vehicle forward or backward. For example, in a front-engine, front-wheel-drive car, the power of the engine is transmitted to the front wheel hub assembly through the gearbox, drive shaft and other components, which in turn drives the front wheel to rotate and propel the vehicle.
Non-driven wheel hub assembly: Mainly installed on non-driven wheels, such as the rear wheels of front-wheel-drive vehicles and the front wheels of rear-wheel-drive vehicles. Its main function is to support the weight of the vehicle, ensure that the wheels can rotate freely, and assist the vehicle in steering.
(II) Classification by structural form
Traditional split wheel hub assembly: In this type of wheel hub assembly, the wheel hub and bearings and other components are assembled separately. During installation and maintenance, each component needs to be operated separately, which is relatively complicated. However, its structure is simple and the cost is low, and it is widely used in some economical vehicles.
Integrated wheel hub assembly: With the continuous development of automobile technology, integrated wheel hub assembly is becoming more and more popular. It integrates components such as wheel hubs, bearings, sensors, etc. to form a compact whole. This design not only reduces the number of parts and components, reduces the difficulty of installation and maintenance, but also improves the overall performance and reliability of the wheel hub assembly.
IV. Manufacturing process of wheel hub assemblies
(I) Casting process
Gravity casting: This is a relatively traditional and simple casting method. Liquid metal is injected into the mold cavity under the action of gravity, and the wheel hub blank is formed after cooling and solidification. The advantages of gravity casting are simple equipment and low cost, but due to the slow flow of liquid metal in the mold, it is easy to produce defects such as pores and shrinkage, which affect the quality and strength of the wheel hub.
Low-pressure casting: In a low-pressure environment, liquid metal is injected into the mold cavity by pressure. Compared with gravity casting, low-pressure casting can make liquid metal fill the mold more quickly and evenly, reduce the occurrence of defects such as pores, and improve the quality and dimensional accuracy of the wheel hub. At the same time, the production efficiency of low-pressure casting is relatively high, which is suitable for large-scale production.
High-pressure casting: Liquid metal is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure at high speed, so that the metal solidifies and forms under high pressure. High-pressure casting can produce wheels with complex shapes and high dimensional accuracy, but its equipment investment is large, the requirements for molds are also high, and the metal liquid is easily involved in the gas due to the excessive filling speed, which affects the quality of the wheel.
(II) Forging process
Forged wheels are forged by forging metal billets to make them plastically deform under pressure, thereby obtaining the required shape and performance. The forging process can make the internal structure of the metal more compact and improve the strength and toughness of the wheel. Compared with cast wheels, forged wheels are lighter and stronger, but the manufacturing cost is also relatively high. They are mainly used in high-performance cars and some high-end models.
As an important part of the vehicle's driving system, the performance and quality of wheel hub assemblies are directly related to the driving safety and overall performance of the vehicle. It is crucial for every car owner to understand the relevant knowledge of wheel hub assemblies and do a good job of daily maintenance and maintenance.